Cohere Showcases How LLMs Are Transforming Retail Customer Experiences
May 17, 2024 — Cohere has published a new article discussing the transformative potential of large language models (LLMs) in the retail industry. In the post, David Stewart, Robin Gainer, and Sam Barnett highlight four critical areas of the retail value chain: customer service, marketing and sales, logistics and distribution, and employee experience. Last week, Cohere introduced fine-tuning for Command R.

From logistics to customer care, LLMs can fuel better shopping experiences and help retailers transform economic headwinds into tailwinds to achieve greater growth.
First rule of retailing: the customer comes first.
Any new tech that serves to improve customers’ experience — from how they interact with a brand to the support they receive — is essential for driving revenue. No wonder retailers are eagerly embracing large language models (LLMs) to enable new and improved solutions across the entire retail value chain.
The potential ROI is enormous. Generative AI (GenAI) solutions, which use LLMs for advanced natural language processing capabilities, can deliver a staggering $660 billion in value to retailers and consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies. With economic headwinds, labor shortages, and competitive pressures weighing heavily on the industry, GenAI offers retailers a pathway for greater growth.
This is all thanks to AI models, like Cohere Command R, that can swiftly synthesize vast amounts of data, create new content, and streamline customer service. And, when the models are empowered with sophisticated reasoning capabilities that can autonomously execute tasks, they become powerful AI agents. Simple tasks, such as automatically updating a customer’s account following an online service request, are just the beginning. More complex workflows and automations to improve customer services can quickly follow.
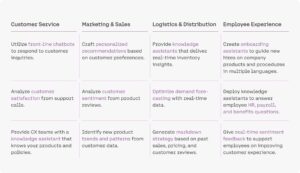
In this article, we highlight four areas of the retail value chain — customer service, marketing and sales, logistics and distribution, and employee experience — where GenAI has already begun to transform the customer experience. We also offer insights into how the next generation of autonomous AI agents may soon enable retailers to leapfrog their competitors.
Delighting Customers with Faster, Better Service
Let’s start with the use of LLMs in customer service, given the massive impact expected from LLMs on retail operations. Most people can quickly rattle off their frustrations with customer service experiences, such as long hold times, slow responses to product inquiries, and getting different answers from different reps about an issue. And the costs of these frustrations can quickly add up.
Across industries, it’s estimated that a whopping $3.7 trillion is lost because of customer service issues. More than half of customers say that customer service outweighs product affinity when deciding which companies to do business with.
For retailers, LLMs are game-changing. They power AI solutions like virtual assistants that help customer service teams tackle these nagging problems and provide customers with a smoother, happier shopping experience.
- Precision Picks Increase Sales. A major luxury goods retailer, for instance, equips its customer advisors with a conversational AI shopping assistant that can accurately suggest products based on a customer’s demographics, purchase history, and personal preferences. Built using Cohere Command and our retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline, including Cohere Embed and Cohere Rerank, these assistants can deliver more personalized and precise recommendations to customers. As a result, the retailer’s customers are signaling their delight by increasing the average size of their shopping basket.
- Rapid Response at Scale. Another popular application of LLMs in customer service is the use of GenAI to answer support questions. Previous chatbot solutions often struggled to find the right answers when customer questions deviated from standard FAQs. LLMs, on the other hand, are great at deciphering intent from natural language queries. These conversational AI assistants can respond to tens of thousands of customer questions on everything from guiding a customer through the return process to answering questions on recent promotions. Some companies are already on course to realize tens of millions in savings and report higher customer satisfaction using these AI assistants.
As brands compete on customer service, there’s no time to waste. We’re seeing retail leaders rigorously testing LLM solutions internally to achieve the best cost-performance balance. This can be an iterative process, where companies often need to explore several approaches, models, and tools before landing on the optimal solution.
During such explorations, it’s critical to understand the implications of different models, including type, size, source, and deployment options. These choices can significantly impact the ROI, accuracy, and speed of models as usage scales. Solutions like the Cohere Toolkit, an open-source repository of production-ready applications deployable across different environments, can help retailers accelerate development and begin testing new AI assistants within a few days.
As early adopters expand their use of LLMs to build more sophisticated AI agents, they’ll be upping the ante even further. Consider, for example, a common customer question, like “Where’s my order?” AI agents will not only be able to ask for an order number and check the order management system for the status, but also problem-solve when unexpected delays occur. This might include navigating multiple steps, such as checking that the item is still in stock, adapting its responses based on available inventory, and asking the customer for additional information to expedite a new shipment.
- One Vibe for Seamless Interactions. For global retailers, a big priority is ensuring that all marketing content is on brand and all global reps are trained to deliver the best brand experience. Businesses with operations worldwide often find it challenging to maintain their brand’s tone, style, and other nuances across potentially dozens of languages. And quickly onboarding staff around the world can be difficult and time-consuming. LLMs with strong multilingual capabilities that can capture cultural nuances like never before can greatly streamline this work, helping marketers deliver best-in-class communications and training across regions.
- Global Trends, Local Insights. But that’s not all. These models can also understand the intent and nuances of customer feedback in local languages. For instance, with models optimized for multilingual usage, like Command R+ and Cohere Embed, global retailers can more effectively extract insights from customer comments on support tickets, reviews, and third-party sources across their markets worldwide to better understand customer preferences and dislikes, and global trends.
Soon, retailers will be able to deploy global AI agents that can connect with CRM, e-commerce, content management, and email marketing systems in any language to understand customer preferences and automatically tailor marketing communications accordingly. Given the abundance of SaaS-based GenAI solutions primed to incorporate agentic capabilities into their products, such advanced use cases will likely become table stakes in the retail industry.
Simplifying Logistics and Distribution Challenges
Ensuring that products are readily available and priced just right is the backbone of a great customer experience. But there are a lot of moving parts that retailers must deal with to get this right. Disruptions due to weather, political instability, and other logistical issues can impact product availability. Changes in market conditions can impact how much consumers are willing to spend on a given product category. Economic shifts, such as changes in interest rates, can impact consumer spending and make yesterday’s forecast irrelevant.
LLMs are enabling logistics and distribution teams to more effectively manage these continuously shifting variables to make sure that the right products are available at the right time. The days of checking different tools and using the correct lingo for each tool will quickly become obsolete, with new solutions providing a unified interface.
- Fine-tuned Inventory Forecasts. One large European retailer, for instance, is tapping Cohere Command R tool use functionality to create an AI agent that can check inventory management systems. This provides merchandisers, buyers, inventory managers, and other stakeholders with accurate, real-time insights about product levels at stores, or popular items at specific times, all with simple, conversational language. Next, the company plans to expand the model’s capabilities to execute multi-step, complex workflows using a variety of tools across several application programming interfaces (APIs).
- Weatherproofed Supply Chains. Another thorny problem that AI agents could help retailers with is planning for an upcoming weather event that might impact the arrival of new merchandise, which can chip away at customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. Here’s how it works: A supply chain manager prompts the AI agent for assistance in understanding the storm’s impact. The AI agent then checks the relevant systems to assess open orders for suppliers who may be hit by the storm and, when needed, identify alternate suppliers who can help the company continue to meet customer expectations. Once the supply chain manager reviews and approves the updated orders, the AI agent could then adjust orders and notify all affected suppliers, as well as customer service teams.
Boosting Employee Experience for Happier Customers
Research has shown a direct tie between employee experience and customer experience, with those ranking highest in employee experience metrics realizing higher revenue and profits. It makes sense. When employees are bogged down with mind-numbing, manual tasks or can’t easily find the information they need, they’re likely to be rushed, distracted, and unprepared when a customer needs help. GenAI’s ability to take on the grunt work and improve employee productivity can pave the way for greater job satisfaction, and, ultimately, better customer satisfaction.
- Time-saving HR tool. Take a large North American retail chain, for example. The company created an AI knowledge assistant that provides HR, payroll, and benefits information. The solution uses Cohere Command with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is optimized for search with Cohere Rerank. For employees, the AI knowledge assistant gives them personalized answers to their questions based on their location, union affiliation, and job level, all within minutes. And store managers no longer have to spend time tracking down the information, which previously took them weeks of effort.
- Less Searching, Better Service. Another example is the use of conversational AI assistants to more effectively support employees throughout their day. One retailer uses an AI knowledge assistant to help its store associates more quickly get answers to questions on company products, policies, and procedures, so they can better serve customers. Providing new hires with such capabilities can prove especially valuable given that training, support, and reduced productivity while learning the ropes traditionally represent a significant portion of onboarding costs.
AI assistants can also handle other complex operational tasks, which frees up retail associates and managers for more customer-facing activities. One such use case is managing employee schedules, typically a big headache for store managers. Using AI agents that can coordinate multiple back-end processes and ask for more information, employees can more easily make requests for time off. Likewise, managers can quickly access staffing schedules or approve change requests without needing to navigate through clunky internal systems.
Looking ahead, the potential of AI agents to transform the employee experience is vast. With retailers eyeing GenAI en masse, we expect to see some amazing advances in customer experience. Sometimes, it’s the simple solutions to frustrating everyday problems that make the biggest difference. Combining LLMs with agentic capabilities opens immense possibilities across the retail value chain in solving the many issues (big and small) that make customers unhappy. In this dynamic landscape, it’s either stay ahead or risk losing customers.
Source: David Stewart, Robin Gainer and Sam Barnett; Cohere